| Home | Products | Tools | Technical Resource | Catalog Order | Custom Oligo Order |
 |
|
Technical Sheet
Catalog Number: 40-2015-10 500 ng Shipped at ambient temperature. Store at -20o For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures; for clinical purposes only. |
|
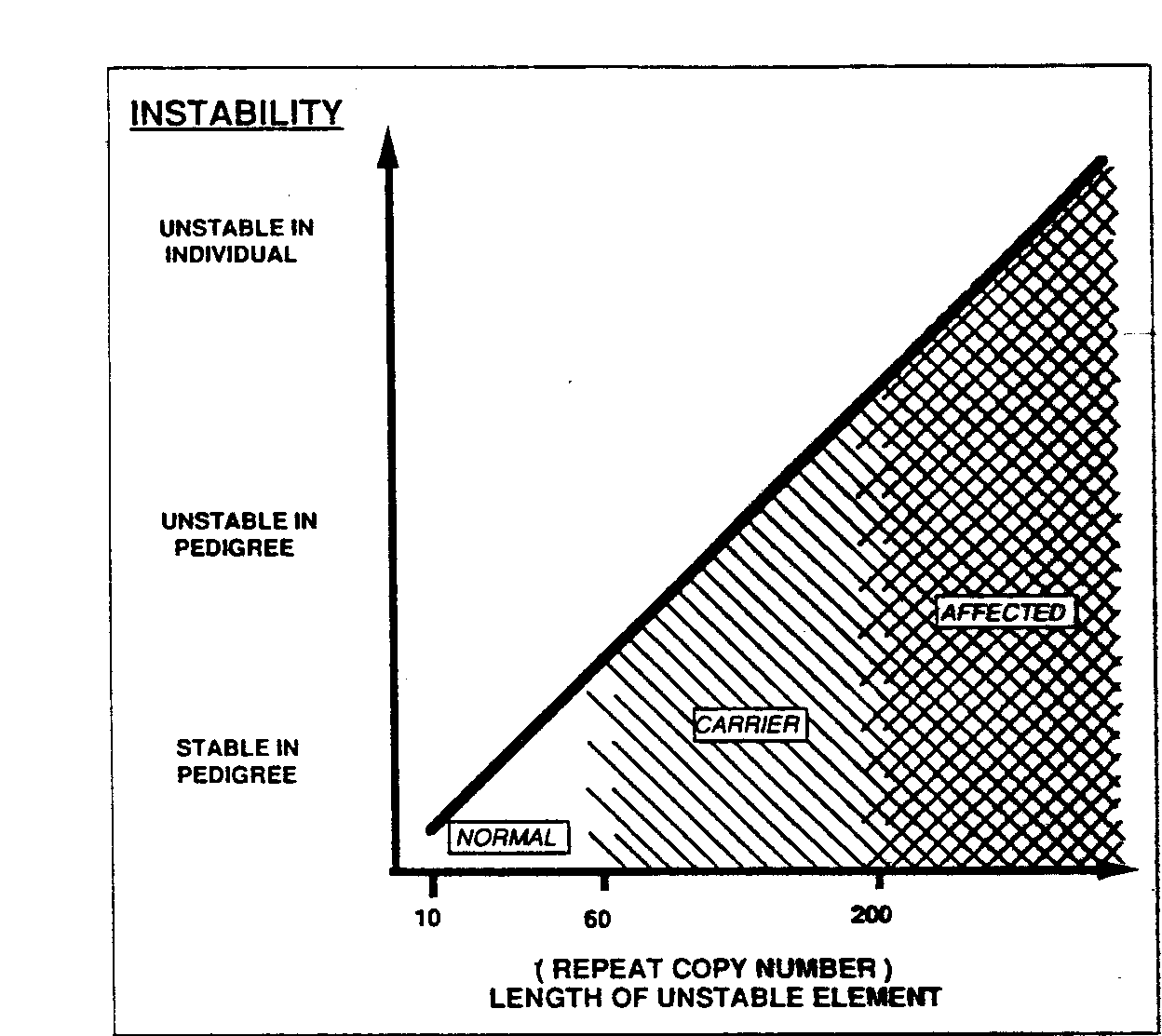
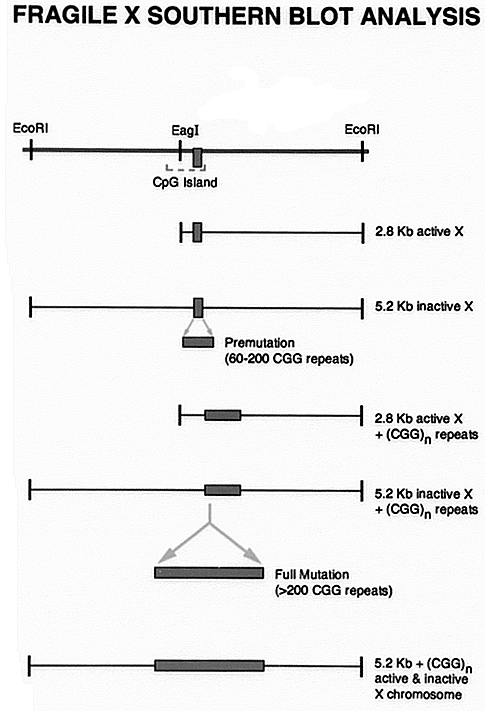
Background Fragile X syndrome is the most common form of inherited mental retardation. It affects approximately 1 in 1200 males and 1 in 2500 females. As suggested by the name, it is associated with a fragile site under specific cytogenetic laboratory conditions at position Xq27.3 (1). The inheritance pattern of fragile X puzzled geneticists as it did not follow a clear X linked pattern. Approximately 20% of males who are carriers based on pedigree analysis do not manifest any clinical symptoms and are thus termed as Normal Transmitting Males (NTM), mental retardation is rare among the daughters of male carriers. Approximately 35% of female carriers have some mental impairment. Based on the above it has been proposed that there are two states of the mutation, one mutation range in which there is no clinical expression (premutation), which could change to the disease causing state predominantly when transmitted by a female (full mutation)(2). The fragile X syndrome gene (FMR-1, fragile X mental retardation -1) was cloned in 1991 simultaneously by three groups (3-6). Soon the peculiar genetic mode of transmission was established and a new class of mutation came into existence- Triple repeat amplification. This explained the clinical state of ‘premutation’ and ‘full mutation’ as well as ‘anticipation’. The fragile X syndrome is caused by the amplification of CGG repeat which is located in the 5’ region of the cDNA. The most common allele in the normal population consists of 29 repeats, the range varying from 6 to 54 repeats. Premutations in fragile X families showing no phenotypic effect range in size from 52 to over 200 repeats. All alleles with greater than 52 repeats are meiotically unstable with a mutation frequency of one. In general repeats up to 45 are considered normal, repeats above 50 to 200 are considered as premutation and above 200 as full mutation (3-7). The range between 40-55 is considered even by most experienced clinical geneticists and molecular geneticists very difficult to interpret and is considered as a ‘gray zone’ with interpretations made on a case by case basis (8). Genotyping Fragile X genotyping can be done by direct PCR amplification of the CGG triple repeat region or by southern analysis. In most cases both methods are used to complement the results, full mutations usually cannot be identified by PCR by most investigators and southern analysis is the preferred method to distinguish full mutations. The FMR-1 gene region containing the CGG triple repeat is flanked by Eco RI sites and a Eag I site in the region. Full mutation has been shown to methylate the active gene too and thus it prevents Eag I restriction of DNA. Hybridization of southern blots of Eco RI and Eag I double digested DNA clearly can distinguish between normal, premutation and full mutation genotypes (2).
Southern analysis can not determine the exact number of repeats or the identification of genotypes corresponding to the ‘gray zone’ . |
References
|
**The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process is covered by patents owned by Hoffmann-La Roche. A license to perform is automatically granted by the use of authorized reagents.
All Gene Link products are for research use only.
Appendix
Material Supplied One tube containing 500 ng of lyophilized Fragile X/GLFX1 probe. The DNA probe is stable in dried state for extended period at room temperature. Upon reconstitution it should be stored at -20 oC. The quantity supplied is sufficient for at least 5 random prime labeling reactions using 100ng for each reaction.
Fragile X Southern Protocol
1. DNA digestion : DNA 10 mg10x Eag I Buffer 10 ml10x EcoR I Buffer 10 mlEag I (10 U/ ml) 4 mlEcoR I( 10 U/ ml) 8 ml------------------------ H2O up to 100 mlPrecipitate the digests after over night digestion at 37oC, dissolve the pellets in 10 ml of 1x Loading buffer .2 Load samples to 0.8% agarose gel , run over night at 45mA for ~24 hours. (1.6 kb fragment on the bottom of the gel).
3. Depurination with 0.25N HCl (add 10 ml HCl to 500ml H2O) for 10 minutes, denature the DNA with 0.4N NaOH/0.6M NaCl for 30 min. at RT, neutralize with 1.5M NaCl/0.5M Tris ( pH 7.5) for 30 min. at RT, transfer to the MagnaCharge Nylon membrane (MSI) by 10xSSC and 10 pieces of SIGMA QuickDraw blotting paper over night. Wash the membrane with 2x SSC, bake it at 80oC for 2 hours. |
4. Perform prehybridization at 50oC for 3 hours in 10 ml of hybrisol I buffer (Oncor) .
5. Label the probe as following: ( BM Random Primer DNA Labeling Kit) GLFX1 GeneProbeä 25 -100 ng H2O up to 9 mlBoil 10 minutes, and put on ice. Add : Reaction mix 2 mldNTP w/o dCTP 3 mla 32PdCTP (3000 Ci/mmol) 5 ml (50 mCi)Klenow (2 U/ml) 1 ml -------------- Total 20 mlIncubate at 37oC for 30 minutes. Add 500 ml of 5 x SSC to the reaction tube, boil 5 minutes, then add to the 50 ml Falcon tube containing the membrane and hybrisol I solution, mix well, incubate in shaking waterbath at 50oC over night.6. Wash the membrane in 2 x SSC/ 0.1% SDS at RT twice ( 5 min per wash)., then wash with 0.1 x SSC/ 0.1% SDS at 60oC twice (30 min. per wash). Wrap the membrane and put X-ray film on it, expose at -80oC over night. Develop the film next morning.
7. Strip the membrane by incubating in 0.5 N NaOH for 1 hour at RT with constant agitation. Change the solution and incubate over night if necessary. Rinse the membrane with 2x SSC, air dry. |
Ordering Information
| GENEMERä | |||
| Product | Size |
Catalog No. |
Price |
| Sickle Cell SC2/SC5 primer pair | 10 nmoles |
40-2001-10 |
$100.00 |
| RhD (Rh D gene exon 10 specific) | 10 nmoles |
40-2002-10 |
$100.00 |
| Rh EeCc (Rh Ee and Cc exon 7 specific) | 10 nmoles |
40-2003-10 |
$100.00 |
| Fragile X (spanning triple repeat region) | 10 nmoles |
40-2004-10 |
$100.00 |
| Gaucher 1226G mutation specific | 10 nmoles |
40-2005-10 |
$100.00 |
| Gaucher 1448C mutation specific | 10 nmoles |
40-2006-10 |
$100.00 |
| Gaucher 84GG mutation specific | 10 nmoles |
40-2007-10 |
$100.00 |
| Gaucher IVS2 mutation specific | 10 nmoles |
40-2008-10 |
$100.00 |
| Cystic Fibrosis D F508 | 10 nmoles |
40-2009-10 |
$100.00 |
| Cystic Fibrosis G542X | 10 nmoles |
40-2010-10 |
$100.00 |
| Cystic Fibrosis W1282X | 10 nmoles |
40-2011-10 |
$100.00 |
| Cystic Fibrosis G551D/R553X | 10 nmoles |
40-2012-10 |
$100.00 |
| Cystic Fibrosis N1303K | 10 nmoles |
40-2013-10 |
$100.00 |
| Cystic FibrosisCT3849 | 10 nmoles |
40-2014-10 |
$100.00 |
| SRY (sex determining region on Y) | 10 nmoles |
40-2020-10 |
$100.00 |
| X alphoid repeat | 10 nmoles |
40-2021-10 |
$100.00 |
| Y alphoid repeat | 10 nmoles |
40-2022-10 |
$100.00 |
Please inquire about other GENEMERä not listed here |
|||
**The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) process is covered by patents owned by Hoffmann-La Roche. A license to perform is automatically granted by the use of authorized reagents.
Prices subject to change without notice
All Gene Link products are for research use only.
Copyright Gene Link, Inc 2002. All Rights Reserved. For any help, please direct all inquiries to The Webmaster.